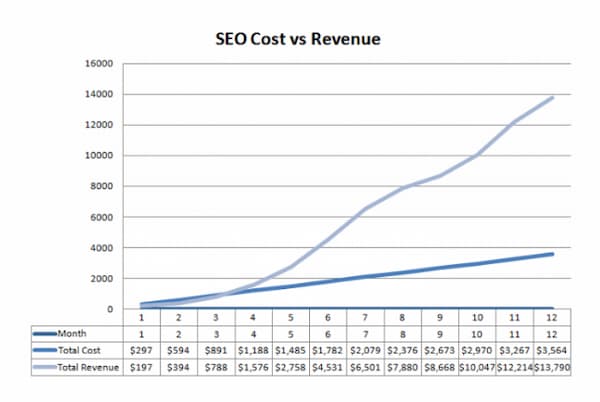
What’s the point of owning a website if no one can find it online? Your website is your means for educating an audience and generating leads. You can’t drive new business unless new users are landing on your pages. At a bare minimum, you need to apply SEO basics.
Here’s an old SEO joke: Where do you hide a dead body so no one can find it?
A: On the second page of Google!
More than 90% of users click on the first page of search results. That means that if your website appears anywhere other than the first page, you’re missing out on more than 90% of new client opportunities.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is search engine optimization (SEO)?
SEO is the process of improving the search visibility of a web property for specific keyword search queries. The process includes a number of different tactics and strategies that are intended to improve the likelihood of a web page being displayed as the best solution to a search result. Ideally, this results in the page appearing at the top of the search results.
The overarching goal of SEO is to increase revenue
The ultimate goal of SEO is to increase revenue by driving more traffic to a website. Search engines assess the quality of web pages using a number of different factors. Improving the SEO of a web page increases the number of positive ranking factors that lead to higher search engine rankings and increased search visibility.
SEO separates your content from the masses
Did you know that there are over 2 million WordPress blog posts published each and every day? That means that more than 20 blogs are published every second. Considering the vast number of blog post being published, how can you publish an article and expect people to find it?
That’s where SEO comes into effect. For every person who searches Google, they are required to enter a word or phrase that describes what they’re looking for. When your page is optimized to answer the intent of a user (referred to as search intent), your answer is more likely to appear on the search engine result page (SERP).
What is user intent/search intent?
Search intent is the underlying reason a user initiates a search. Satisfying search intent refers to the content that will put an end to a user’s search. This concept is extremely important to SEO because Google has been able to accurately interpret user intent and assess web pages to determine whether they are able to satisfy search intent.
Optimize for search intent to increase user engagement
To be the best solution to search query, your page not only needs to be optimized for the query, but it needs to be accurate and adequate in the content it serves. If users click on your page and then back off of it, it indicates low user engagement. The metric used to measure the number of users that land on your page and back off is known as bounce rate.
(Click here to read 9 Ways To Reduce Your Bounce Rate)
This is an important user engagement statistic because it alludes to whether users find your page relevant to the search query. When people refuse to stay on your page for more than a second, but they spend time on a competing page, the competing page will more than likely rank ahead of the page no one wants to spend time on.
For this reason, keywords and content play a massive role in determining how search engines assess your page and display it in the search results.
How does SEO work?
SEO is a process that combines keyword research, content creation, on-page optimization and off-page optimization, data-driven analysis and technical performance for the purpose of increasing traffic for lead generation. The end result is keyword-optimized pages that receive more visitors from improved search visibility.
SEO identifies the traffic opportunities available and works towards implementation to achieve a regular flow of traffic from organic keyword rankings (and paid traffic) that results in more leads, new clients and increased revenue.
The role of keywords
The words that a user types into a search are considered keywords. SEO is primarily keyword based due to the way users search for information. A typical SEO campaign involves publishing pages that are optimized for specific keyword searches. This makes keyword research one of the most important aspects of developing an effective SEO strategy.
The keywords your website appears for should benefit your business by attracting visitors that have or will have intentions to buy the product or service you offer. What’s the point in ranking for a keyword when the visitors aren’t ever going to buy from your company? Keyword research is a process that results in the confirmation of what is actually being sought after in a search, and what content you need to provide to satisfy that intent.
Keyword research
Keyword research establishes the true search intent of a search phrase. It’s not just about avoiding a terrible mistake, but also identifying the content required that would propel your web page to the top of the search results.
If you’re going to rank in the best positions you need the best content.
The process involved in researching keywords requires you to go through a series of steps that provide hints and clues to what will make the best content for the search term in question.
Create a list of potential options
An easy way to start your keyword research is to make a list of the words that you want your website to be known publicly. These initial terms can describe your business and are most likely products and services.
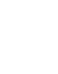
Generate more ideas with Google autosuggest
Type these phrases one by one into Google and write down any relevant keywords that appear in autosuggest.
Confirm the business value by analyzing the organic results
For every keyword you consider targeting, you’ll need to check the 10 organic results to see if the competing pages are a match for your business. Google may surprise you with how it interprets intent. The organic results should be direct competitors in your industry.
If there are search listings that are NOT your competition it could be an indication your keyword has diluted search intent. Perhaps not all of the people searching your keyword will be interested in what you offer and another alternative should be considered.
There are endless ways in which you can come up with keyword options. To evaluate a keyword, ask these three questions.
Does the true search intent represent a high business value?
Search intent is the biggest factor because you need to determine whether the content that currently ranks for the keyword is something that would benefit your business. If there’s no value in the keyword then it doesn’t make sense to waste your time and effort in creating the content.
How much volume makes a keyword worthwhile?
You can drive 50K visitors to your site but if no one converts to a new client the volume of traffic from that keywords is useless. If you can drive 20 people from a keyword and 5 of them end up making a purchase, you’ll need to assess the number of resources needed to acquire those 20 people on a regular basis.
If the traffic from a keyword results in high ticket purchases, then even keywords with low monthly search volume are worthwhile in pursuing.
The bottom line: Volume is ony as important as the business value of the keyword in question.
How difficult is it to rank your content on the first page for that keyword?
In a perfect world, we want high converting keywords that have tons of monthly searches and zero competition. Since this is rarely the case for any keyword the strength of the competition needs to be weighed in against the business value and volume of searches.
If the websites on the first page have been around for years, there’s a good chance they’ve accumulated a lot of backlinks and have made a name for themselves in the industry. When all 10 organic results are competitors with massive domain authority, there is little to no chance for a newish website to rank ahead of them and so it would make sense to consider another option.
Find alternative keywords when the competition is difficult. You can choose a synonym or related keyword, or you can use a long-tail version of the keyword you initially wanted to pursue.
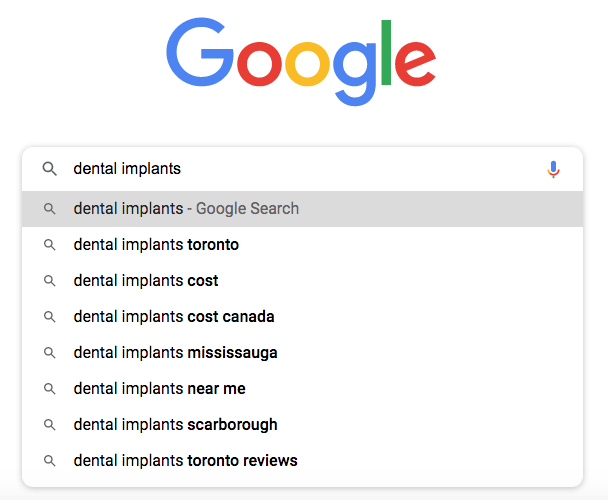
Reduce competition using long-tail keywords
Three or more words used as a search term are considered a long-tail keyword. The majority of searches made on Google (70%) are long-tail keywords.
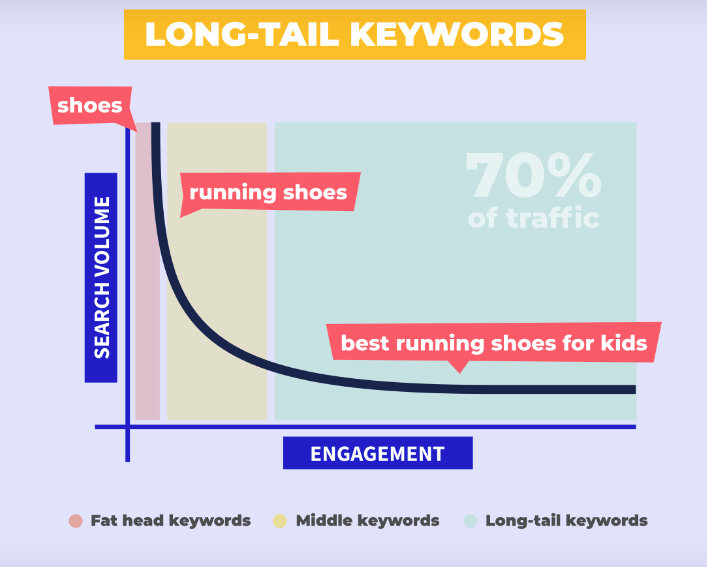
Increase conversions by targeting long-tail keywords
Most people try to describe what they are looking for in more detail when they know what they want. This means that long-tail keywords convert at a higher rate than head keywords (one to three words used in a search term).
The more words a person uses to describe what they are looking for, the more you can provide an accurate match as a solution to search intent. The benefits of long-tail keywords are:
- Higher engagement statistics
- Higher conversion rates
- Lower competition
The only downside to optimizing for a long-tail keyword is that they typically have less search volume. That being said, it’s better to get 10 people to buy your product out of 50 than it is to get 1 person out of 1000.
It’s much easier to nail search intent with long-tail keywords because the focus is much narrower.
For example, if a user were to search for summer shorts, there are a vast amount of options that this keyword could possibly mean. Does the user want spandex, cotton, nylon, a specific colour, style or fit?
If your website doesn’t sell every single option a visitor might be looking for when they search summer shorts, then driving traffic from this keyword would lead to high bounce rates and ultimately poor search visibility.
If your business only sells cotton shorts with various camouflage patterns, there would be no sense in optimizing for the keyword summer shorts, when you would have more success with terms like camouflage shorts or army shorts or more descriptive search terms.
When your products or service has a narrow focus, it’s a better approach to optimize for more accurate keywords.
Establishing a keyword strategy
Your keyword strategy should consist of keywords that are exact matches to your products and services to drive traffic with visitors with buyer intent. Your strategy should also include keywords that address the most commonly asked questions, common problems and the answers to those issues.
This type of strategy affords you the time it takes to rank for more difficult terms while ranking faster for long-tail phrases that ultimately lead to visitors on your main pages.
By assigning keywords topically, you can address more relevant issues and then find the best keywords that match your business through data-driven analysis.
Keyword tools are the most convenient at this stage of the process and can help finalize your target keyword in the content you publish.
Content Creation
To get your content to rank and outperform competing pages, it needs to be the best response to a search query. A large part of creating content that performs is figuring out whether you’re going to publish something unique, or whether you’ll publish something that’s just better than what’s already out there.
Analyze the top ten results for clues on search intent
One of the biggest clues to establishing search intent is in the page titles of the top ten organic results. The titles will show you what type of content has the best possibility of ranking highly.
Take the search term, how to rank a website for example.
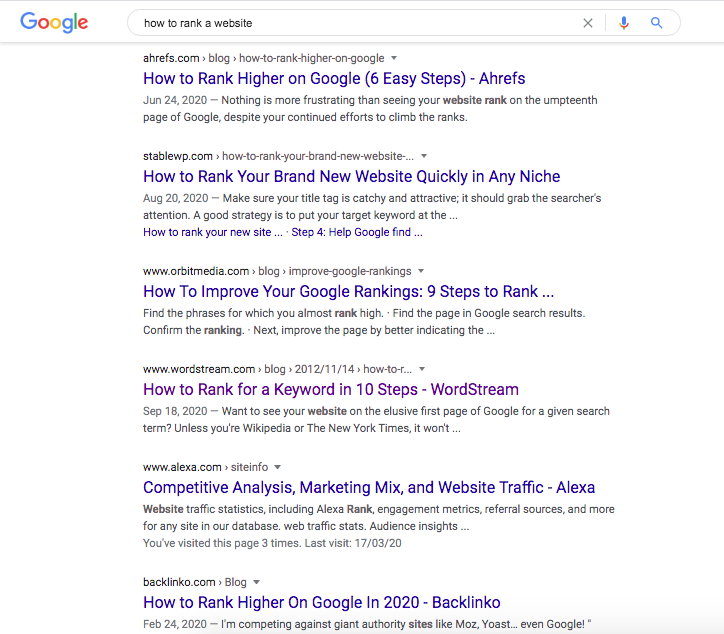
Out of 10 search results, 7 have titles that start with “How-to” indicating that the type of article users click on the most are how-to articles. This example is super obvious but the same holds true for any keyword in question.
Another example is to try searching the term drive more traffic.
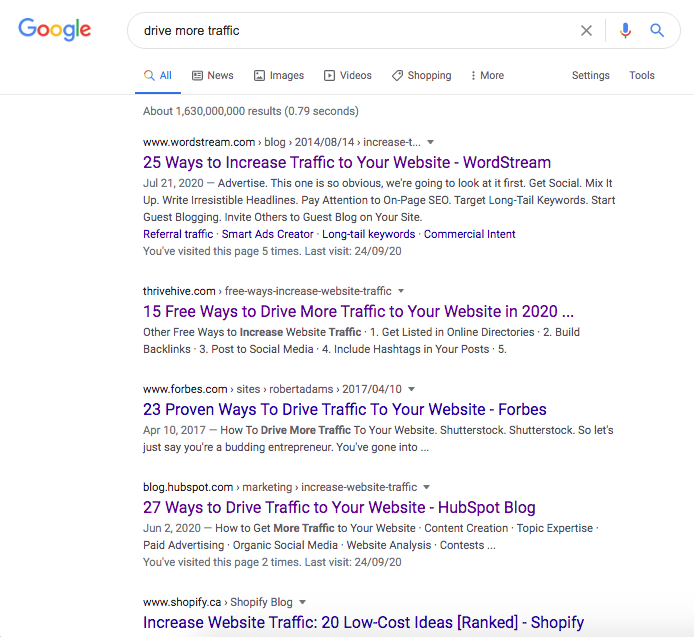
Again, 7/10 search results have titles with numbered lists that detail the different ways to drive traffic to your website. Evidently, the best opportunity to rank for this search term is to produce an article with a numbered list.
Analyze SERP features to improve your solution to search intent
There’s no one who understands search intent better than Google. Take into account the various SERP features that appear for your keyword. You can use the appearance of SERP features as clues to publishing content that is optimized to satisfy user intent.
Extract topically relevant questions and answers from the People Also Ask Box
The People Also Ask box, for example, is packed full of topically relevant questions that people also search in addition to searching for your keyword. If you can provide the answers to those questions within your page, it’s one less search your visitor would have to make and one more reason for them to stay on your page.
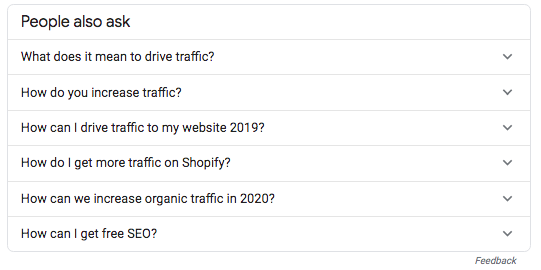
Incorporate the content from the PAA boxes to supercharge the number of topics your content covers as well as commonly asked questions. This content addition will make your page more user-friendly by directly answering popular questions.
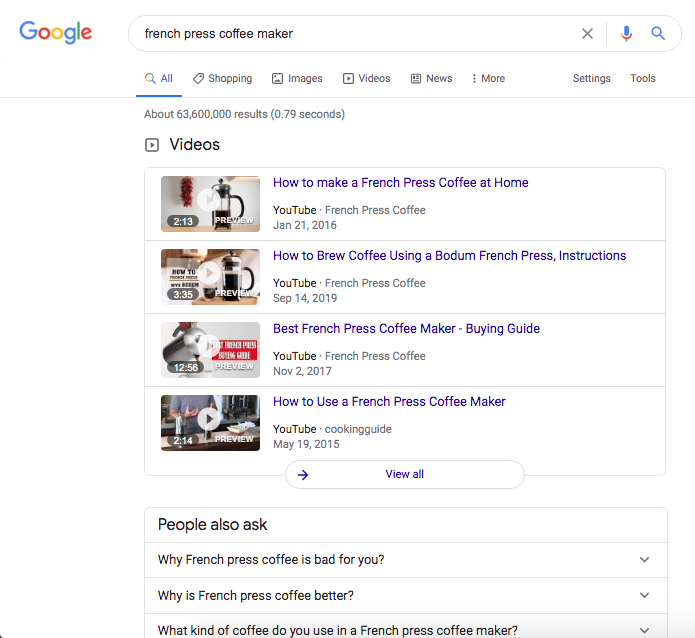
Optimize your page with multimedia
If any videos or images appear directly in the SERP, it’s an indication that users are actively looking for one or both types of media. When Google is displaying a carousel of videos at the top of the SERP, it would improve your pages ability to have a video on your page as well.
Outperform existing content
In order to outperform existing content, you need an accurate idea of what will make your version better than what’s already ranking.
You’ll need to determine the areas in which you can create a better piece of content.
Look to outperform existing content by publishing more in-depth content to better answer intent. Create more user-friendly features that lead to longer dwell time, higher click-through and lower bounce rates.
Reverse engineer top rankings
Create 10x content (content that’s 10 times better than what’s out there) by covering the details of every topic and subtopic on your competing pages.
If you use WordPress, copy and paste one of the pages that rank in the top positions. Click on the information icon to get a full summary of their article for a clear perspective on the word count, the number of topics covered and the hierarchy of content.
The information can provide you with a birds-eye view of how your competitor has constructed their page.
You can also enter a top-ranking URL in any analytic software that generates a keyword report. SEMRush will show you the value of organic traffic for any page.
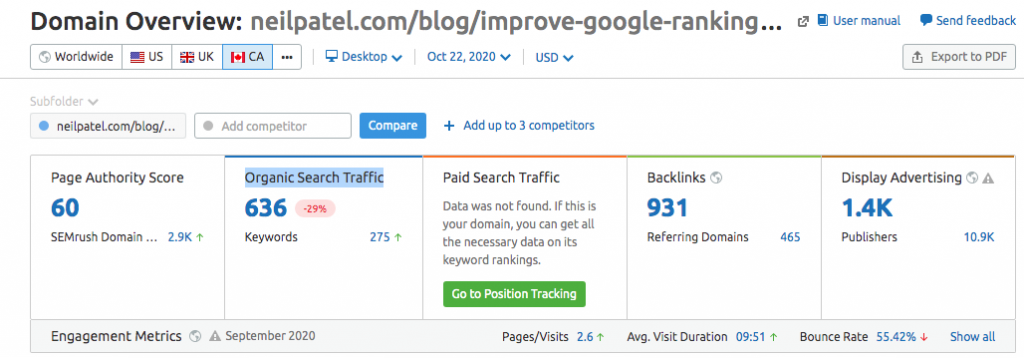
Click on the link and it will take you to another breakdown of all the keywords that URL is ranking for in the top 100 positions.
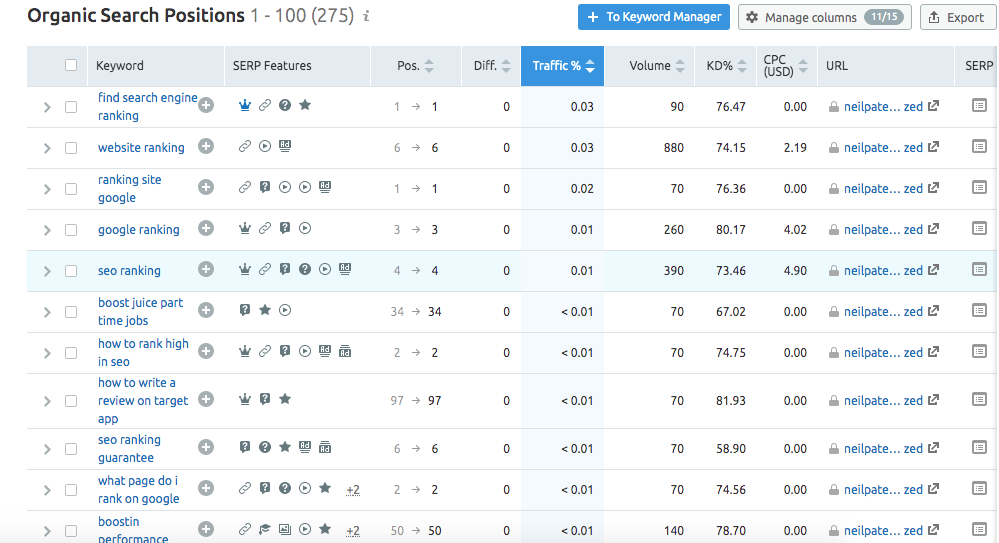
This report gives you insight into any gaps in content your page may or may not have. By identifying keywords you’re not optimized for, you also identify segments of content that will need to be added in order to meet and exceed the quality of the page that’s currently ranking.
Organize your site topically to enhance the performance of major keyword topics
SEO revolves around content because, without it, there wouldn’t be any SEO. Every page on your website should be optimized to target a specific keyword and play a role in driving traffic and converting visitors into clients.
An effective structure to implement in your content creation is to create topic clusters. A topic cluster consists of three different components; pillar pages, cluster content and the links that bind them.
A pillar page is typically a major keyword theme and it covers all aspects of that topic in breadth, but never dives deep into detail. Rather than cover every detail within the pillar page, a pillar page will link out to more narrowly focused articles. These articles are considered cluster content.
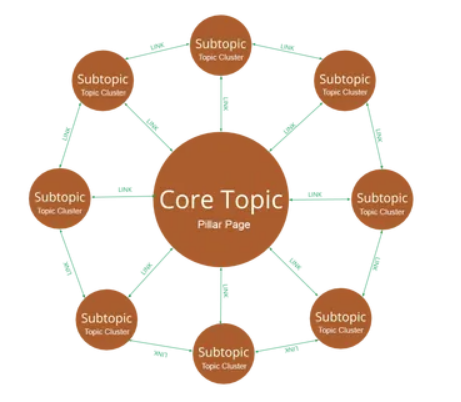
Cluster content, for the most part, targets a long-tail keyword and has a narrow focus on one specific topic. Cluster content goes deep into detail and attempts to fully answer the search intent associated with the keyword it targets.
A pillar page will link out to its cluster content and in return, the cluster content will link back to the pillar page. Cluster content will also link to related content within its cluster. This interlinking strategy is what forms a topic cluster.
The blueprint for your topic cluster is created within your keyword strategy. It begins with brainstorming the most important keywords to your website.
For every major keyword theme break it down into smaller subtopics.
Break down the subtopics into common problems faced by prospective clients. The collection of subtopics should adequately describe your business as well as provide ways for searchers to become aware of your product.
For example, if you were creating a top cluster for your dental practice, you might have the following pillar pages on your website: Cavities, Cleaning, Root Canals, etc.
For each of these pillars you would break down the topic into a number of different subtopics.
For cavities you might include the following as subtopics:
- How to know if you’ve developed a cavity
- Do filling cavities hurt after it’s finished?
- How long does it take to fill one cavity?
Potential keywords could be how patients are describing the pain they have. Keywords posed as questions “Why does my tooth hurt when I chew?”
Whether they know it’s a dental issue or not, a person will type in the symptoms they’re experiencing. Your cluster content would be optimized to address this issue and explain how your services can help them with their problem.
This type of content would be considered top of the funnel content to create awareness in your service or product.
The content you publish on your site should start with the most important pages to your business. The pillars can be category pages, service pages, or landing pages to convert visitors to clients.
Build cluster content to lead visitors to these pages. This can often be done by targeting specific issues (long-tail keywords) as well as publishing comparative content that forces visitors to consider your company as the best choice.
On-page optimization
The contextual meaning of your content can be communicated through the metadata, text, images and structured data markup on your page. Using each of these aspects of your page allows you to highlight the most important keywords you intend to target in the search results.
Metadata
The metadata is extremely important because search engines will read and use this information to categorize your content. Including your keyword in the title, URL, image alt tag as well within the body of content will improve the optimization of your page for a specific keyword.
Text
Use your keyword sparingly in the body of your text. A common mistake website owners make is to repeatedly use the keyword excessive and unnaturally. This will over-optimize your page.
Make sure your keyword appears in the first 100 words or so and a few times within the body of the text. You can use keyword synonyms to enhance the optimization of your target keyword as well as promote a rank for secondary search terms.
Images
Despite the large leaps forward in technology, Google will still use the description in the alt tags as the primary clue for optimization. Use your keyword within the alt tag to enhance the optimization of your page, but this also optimizes the image itself.
Web pages aren’t the only means for driving traffic. Image sources can drive a huge percentage of your traffic if you’ve optimized them correctly.
Include the keyword in the filename, fill out the captions and give your image a descriptive title (avoid using the same words as in the alt description).
Structured data markup
The language of search engines, otherwise known as Schema, clearly communicates contextual meaning and other important information located on your web page. Schema.org has a list of entities that have been defined with appropriate markup and can be used on your page to break down any barriers of communication between search engines and your page.
Apart from providing a faster method of delivering accurate information, Google offers enhanced search results with the right markup. Google displays rich results for markup that informs search engines of reviews, FAQ sections, Q & A pages and How-to articles-just to name the top ones.
Rich results lead to higher click-through rates in the SERP by making your search result more marketable.
Off-page optimization
Anything that affects the optimization of your page, but doesn’t occur on your page is considered off-page optimization. This is largely the process of building external and internal links, but can also include improving technical performance.
Internal links
Internal links are among the easiest links to build because they are links to your page from within your website. Internal links create more link equity between pages, which can improve authority and ranking ability.
For example, suppose you have a page that converts visitors to clients really well. Let’s imagine it’s a product page for an incredible razor that does things that you only imagine in your dreams.
The problem is, it’s difficult to get external websites to link to your product page, so how do you get it to rank and generate traffic?
Enter internal link building.
Based on the topic cluster model, you can create content that external websites would be more likely to link to because they provide objectionable value. An article on 10 Ways To Reduce Shave Time And Frequency would be good content asset and has more rank ability then a page with just a product.
By building links from the pages that generate the most traffic, to the pages that convert at the highest rates, you can increase the number of visitors you convert as well as give your product page more authority to rank.
You can also use internal links to optimize for your target keyword by using a mix of exact match anchor text links as well as long-tail anchor text links and keyword synonyms.
External links
As one of the most powerful ranking factors, external link building can create a top-ranking page-even if your content isn’t technically “the best” stuff out there. With enough websites vouching for your credibility, you can literally rank a page for just about anything as long as you have really good links.
Using keyword-optimized external links will enhance the optimization of your page if done correctly. If you only use exact match anchor text, you may end up over-optimizing your web page. This will send your site back in the search results.
Using a mix of exact match, branded, naked URL and non-optimized anchor text will give your page a good balance of in your backlinks profile and promote a healthy ranking for your target keyword.
Social media marketing
Traffic generation is a huge component of SEO, which makes social media marketing an important aspect of your overall SEO strategy. Building a large audience can serve as a way to drive instant traffic to your web pages and get your content in front of a large number of people.
Despite the fact that links from social media don’t count as followed links, there is some value in the user engagement that social traffic creates. Google rewards pages that have high click-through rates, dwell times and low bounce rates.
The law of averages dictates that the more traffic you send to your pages, the more likely you are to acquire backlinks to high-quality content. Social media can drive the additional traffic needed to get you more backlinks.
The incredible number of users on Facebook is enough to make it an attractive source for marketing your business. Facebook is not the only platform that has proven success in building a business.
Retail sales and B2C marketing do especially well on Pinterest and Instagram. Your target demographic will influence the social media website you choose to implement in your marketing.
B2B sales may have more success with websites like Linkedin.
Social media offers a way to market your product for absolutely no cost whatsoever. If you can produce highly engaging, top-notch content you can build a massive number of followers with absolutely zero investment other than time and effort.
Of course, you can also dive into the paid aspect of social media marketing, after all, you’re targeting the same audience that you want to get reading your content. One of the most effective forms of paid traffic is using retargeting.
Retargeting ads will only re-appear to a user once the user has clicked through to your website. Once that happens, the pixel installed on your site will automatically upload a cookie into the user’s browser. Whenever there’s an opportunity for an advertisement to appear, your ad will reappear for however many times you stipulated in the settings.
This is a highly efficient way of getting people more familiar with your company, which opens them up more to doing business with you.
Technical performance
The technical performance of your website can be improved when you know where to make the improvement. In an effort to monitor the various technical aspects of your website, you can run an audit to determine the page speed, the number of broken links, missing metadata, missing pages, duplicate content and indexing issues.
Page speed
The length of time it takes your page to load can greatly affect user experience as well as your ranking (if it’s excessively slow). You can work on page speed by fixing both on-page elements as well as off-page elements.
Reducing the size of your files, compressing your images, and implementing lazy loading can greatly reduce the time it takes your page to load.
You can also use a CDN, inline the HTML, CSS and JavaScript in the header to reduce the time it takes to load. Leveraging browser caching is another one of many tactics that result in faster page speed.
Reducing errors
Every website eventually begins to generate errors with everyday use. Even if you don’t use your website at all and don’t update it, there will eventually be errors generated from incompatible versions of plugins, themes and browsers.
The accumulation of errors on your site can lead to a reduction in the ranking.
Many of the errors that result in a drop in ranking are based on user experience, such as broken links. When a user encounters a broken link, it’s frustrating and causes a slight problem in the fact that the user needs to back up and decide on where they’re headed again.
Having a missing page on your site results in a 404 error message. This can also look bad on your brand and your company could be misconstrued as having a low-quality website.
Fixing broken links and eliminating missing pages is one of many ways to improve the user experience and overall website performance.
Data driven results
Search engine optimization is a highly effective means of marketing for more reasons than just optimizing your pages to appear first in the search result. SEO involves recording, measuring and tracking results, which can give you better insight when making decisions.
Analytics
Google Analytics is one of the most comprehensive tracking software available that comes absolutely free. Once the tracking code is installed you can monitor the volume of traffic, the origin of that traffic and what those visitors did once they were on your website.
Each month you can see how much your traffic is growing and whether the traffic your building is impacting your bottom line. This can give you insight into the effectiveness of ranking keywords and gauge the impact of any SEO campaigns you’re currently engaged in.
Goals and conversions
Creating goals and conversions in Analytics can contribute to establishing better paths within your site to guide visitors to a preferred action. You can track the pages that users click-through to as well as where they drop off.
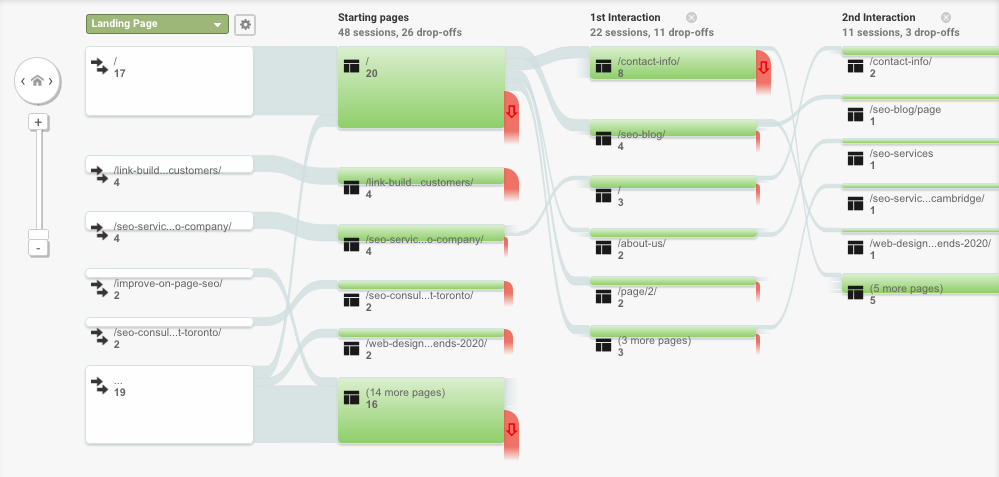
Creating goals is a way to measure the success of your SEO campaigns. By improving on the number of drop-offs you can lead a larger percentage of visitors to pages that help in achieving more conversions and complete more goals.
Compare past and current performance
You can also monitor the traffic on individual pages. This tool allows you to compare any time period with each other to see whether your traffic is above or below the past period’s numbers.
Search console
Search console (another free tool from Google) allows you insight into the performance and health of your website.
You can check to see what queries your pages are appearing for and of those queries how many clicks you earned to your website.
You can build more keyword ideas and content around successful keywords based on the information provided in this tool.
Technical error alerts
The search console informs you of technical errors on your website and will list the URLs of the pages that need work. If your page speed is abnormally slow you can see what pages need improvement.
If your site receives a manual penalty, the search console is the first place to look to confirm whether this has happened. In fact, it’s the first place to look if there’s a sudden drop in traffic since you can see the number of URLs you have indexed as well-just in case the unthinkable is happening and your pages were being taken off of Google’s index (it happens!).
Monitor backlinks
There is a list of the most linked pages as well as the websites that link to you’re the most. You can monitor what backlinks you’re receiving at the fastest time possible since there’s no search engine spider that would know you have a backlink before Google.
Make data-driven decisions
The SEO tools available are numerous and there are more than enough to extract the data you need to make the best decisions for your business. Having insight into the success or failure of specific efforts can save you time and resources in the future.
Analytical tools help to streamline your efforts in creating a more efficient and more effective website that generates traffic leads and new clients.
Implement SEO basics at the earliest stages of development
Search engine optimization is a long-term strategy that can sometimes have quick results. Learn the most important sources of traffic for your business and develop your website to tap into those sources.
Authoritative content is by far the largest ranking factor when it’s optimized to answer search intent. Creating content assets doesn’t immediately translate into massive streams of traffic-there is a period for that content to settle and make its way to the top of the search results.
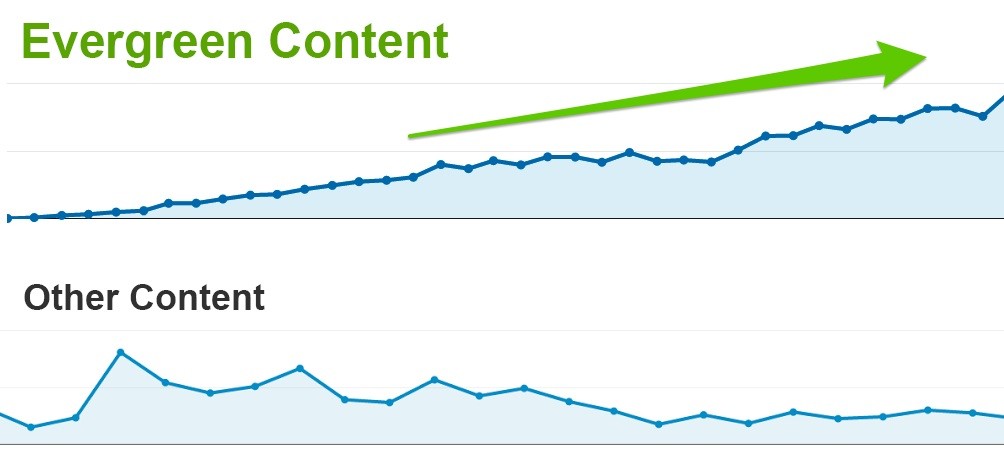
Strategize your keywords, content and link building strategies. The earlier you begin, the sooner you’ll reap the benefits of a well optimized website that generates high converting traffic and contributes to more leads, and revenue.