There could be a number of reasons your site doesn’t show up on Google. Identifying the cause could mean increasing your revenue by thousands of dollars periodically. Here we’re offering you a systematic approach to isolating the problem and applying the correct solution to win you a spot on the first page of Google.
Find the reason(s) why your website doesn’t show up on Google and you will have identified the strategy to take over the top positions for important keywords to your business.
- Failure to answer search intent
- Your keyword is too difficult
- You’re keyword stuffing
- You haven’t optimized your meta tags
- Too many poor-quality links
- Your website lacks credibility and authority
- Your website has thin content
- Your pages are orphaned
- You’ve received a manual penalty
- Your pages are super slow
- Poor user engagement
- There’s been a Google update
- There’s a Google glitch
- Poor choice of anchor text links
- Too early to rank
Table of Contents
Toggle#1-Failure to answer search intent
One of the first considerations (for why your site doesn’t show up on Google) is whether your content completely satisfies the user’s intent for the search. Search intent is a crucial issue because it’s the underlying mandate for a search engine to determine the best response to a search query. Your content needs to satisfy exactly what the user is searching for when they type in a specific keyword.
Satisfying search intent is more than just coming up with your version of content you believe users are looking for when they type in a keyword. It also has to do with what search engines see as the best type of content that answers search intent.
It’s true, there’s a possibility you may be in sync with what users are looking for, but if your pages aren’t ranking you need to look to the top ranking sites to see how they’re satisfying intent.
First clues are in the titles and headlines you see in the SERP. Do the titles indicate a predominant style of content that’s appearing as top results? How many are ultimate guides? How many are “Best-of” lists that provide a user with options?
Pinpoint the way the top ranking pages are satisfying intent and make sure your content covers every aspect and more in the topics that are covered.
Publish content that is 10 times better than what already exists. The skyscraper method has proven to be one of the most effective strategies for outranking and outperforming pages that compete for similar keywords.
#2-Your keyword is too difficult
Many business owners make the mistake of attempting to rank for a keyword without checking the level of difficulty of the keyword. If your website is in its early stages of development, there may be search terms that are not realistic and should be avoided for less competitive options.
Assess the average domain authority
The difficulty of a keyword can be assessed by reviewing the average domain authority held by the competing websites. Domain authority is a form of measuring the ranking ability a domain has that is based on the quantity and quality of links it has accumulated.
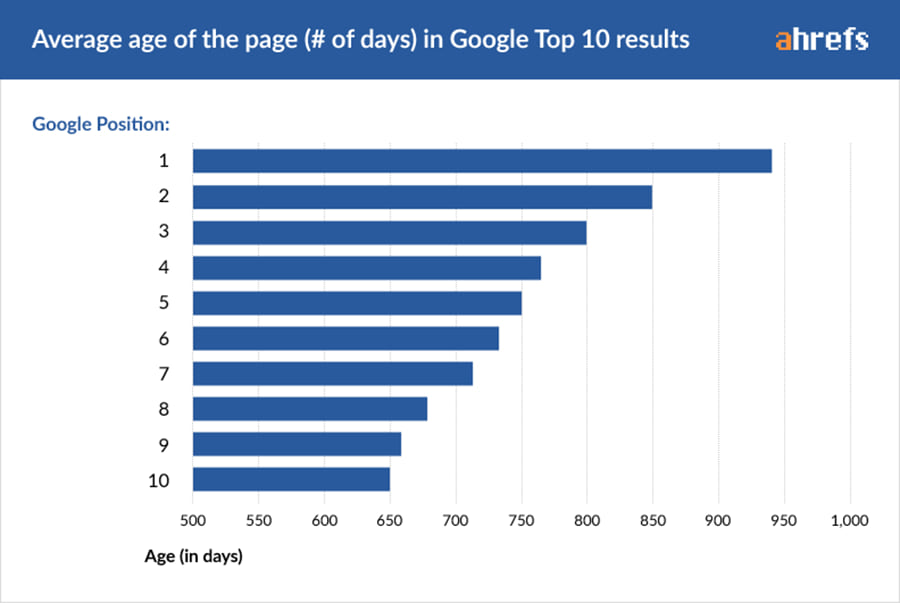
Suppose you were attempting to rank for the search term cheap flights. Your website would be competing with giant authority domains like Expedia and The Flight Network. These websites have been around for years accumulating thousands of backlinks and are considered trusted brands in the industry.
It wouldn’t be realistic to target a keyword that is so competitive without having some sort of competitive advantage that puts you on an even playing field.
Get an idea of the average backlinks pointing to the ranking pages
Search engines don’t rank websites, they rank pages. When you assess the first page of search results, take into account the number of backlinks pointing to each of the ranking pages.
A common trend is that the more domain authority a website has, the fewer links they need to rank its pages. You can use backlinks to increase the page authority of your site in order to compete with domains with greater authority (see image above where Cheapo air has double the backlinks but equal page authority as its competition).
If a website has a similar domain authority to yours, you may be able to beat them by acquiring better backlinks.
You can use Moz to find the backlinks that any given website has pointing to their pages. Make a judgement call on whether it’s realistic to attain the same or more quality links to your page.
Make sure your content meets and exceeds search intent
Even with equal links and domain authority, your content needs to measure up to what’s out there. Make sure your page is able to compete with the competition in the depth of coverage, UX and overall quality.
#3-You’re keyword stuffing
If you repeat a keyword in excess throughout the body of content, it may the reason why your (site doesn’t show up on Google. This is called keyword stuffing and will land you an algorithmic penalty see the Panda update) that prevents your website from ranking highly.
Check to see how many times your keyword is repeated within the body tags of your page (doesn’t include title or URL). Keep your keyword ratio below 2% to avoid over-optimization. If you’ve optimized your meta tags, an exact match keyword need only be sprinkled a few times naturally throughout your content.
#4-You haven’t optimized your meta tags
Place your keyword in the most important parts of the page that search engines use to determine the most important keywords for your page.
Include your target keyword in the title, URL a few times within the body of text as well as in the alt tags of any images on your page.

Use keyword variations in your subtitles and throughout your content to provide more contextual relevance.
#5-There are too many poor quality links
If you have too many poor quality links search engines may devalue the authority of your domain. A low quality link are backlinks that:
- Have no strong relationship to your content.
- Are considered easy to get, such as directory links, profile links, links from forums.
- Have no backlinks itself.
- Have low domain authority.
- Have been penalized
The Penguin update changed how Google assesses link quality and could be the reason why your site doesn’t show up on Google.
#6-Your website lacks credibility and authority
One of the major reasons to acquire backlinks is to build the authority and credibility of your content. Backlinks are a major indication of the popularity of your website.
A backlink represents one website vouching for the content, products or services of another. The accumulation of backlinks therefore builds credibility in terms of many instances of websites vouching for your content.
If your website doesn’t have enough quality referring domains, your credibility for publishing trustworthy content is considered low since there’s no real proof or evidence to say otherwise.
Editorial links from high authority websites that are in the same field of expertise are among the best types of links you can receive. You can build credibility much quicker with much fewer links from sites like these than from low authority websites.
#7-Your website has thin content
Websites that have very little content on their site tend to rank poorly. Without content, it’s hard to get pages to surface at the top of search results for keywords.
Search engines categorize and compare websites to one another in the same niche.
Compare a website with 520 pages of content vs. your website with 3 blog posts. Which one would be more capable of satisfying search intent? Which website appears more trustworthy as an expert in its field?
It’s publicly known that Google reviews specific websites manually to score them on the E.A.T. principles. Expertise, Authority and Trust play an important role in being able to present the top results of a query to users.
There’s some speculation that EAT is baked into the algorithm to an extent already although no one can say for sure. What we do know from documented evidence is that websites that have libraries of relevant content will more often than not outrank websites with thin content.
#8-Your pages are orphaned
Search engines find and index new pages that are submitted in a sitemap or when they crawl websites and discover new pages by following links. If there are no inbound links (internal or external) pointing to your page and it’s not in the sitemap, your page is considered to be orphaned.
Every page on a site should be connected in some way. Ideally there should be a way to get to any page on your website within four clicks. Sitebulb provides a visual way to see how your website is linked through a directory radial such as this:
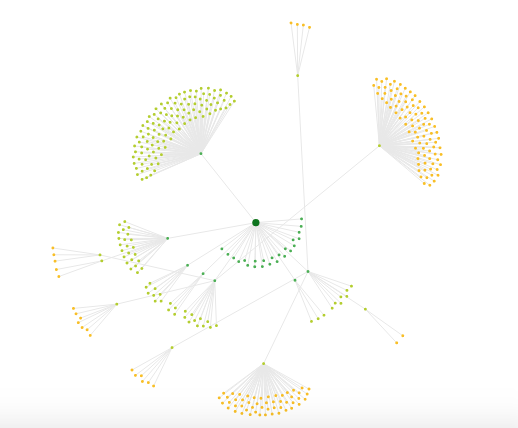
In order to make sure your pages are indexed, they should be included in a fresh sitemap and submitted to Google. Use Google search console to submit new sitemaps as a way of telling Google to index new pages.
It’s best practice to link to new pages you publish in order to connect related content, spread link equity and improve your website’s internal click-through rate. This also allows your pages to be found and indexed faster than waiting for Google to process your sitemap.
If you already have links pointing to those pages, make sure they aren’t marked as nofollow. The nofollow attribute will tell search engines to ignore the link and withhold any transfer in authority that a followed link would give that page.
#9-You’ve received a manual penalty
There are two types of penalties that are commonly referred to; Manual actions and algorithmic penalties. The second, algorithmic penalties are really not penalties per se and are actually just filters baked into the algorithm that can be reversed when you’ve isolated the cause. Manual actions, however, are more severe and usually result in your website being removed from the index.
You can check Google search console specifically to see if any manual actions have been given to your domain. If you received one, you will have specific instructions from Google on why you got it and how to correct the issue.
#10-Your pages are super slow
It’s been years already since Google publicly announced that page speed is an official ranking factor that can affect the search visibility of your website. If your pages are taking too long to load, no one will want to stay on your pages and as a result Google drops your website in ranking.
Rankbrain, Google’s AI that facilitates ranking, measures this user engagement statistic as part of the overall placement of your website. If most of the people landing on your page are backing off of your site immediately, your website is demonstrating signs of a poor user experience and low engagement. That signals Rankbrain to boot your site down in ranking.

You can test your page speed using GTMetrix.com to see if your page clocks in under the recommended time of 2 seconds to the first contentful paint.
Almost every page speed tool generates a report on the elements that are blocking your site from loading quickly. Improving your page speed becomes a matter of being able to execute the corrections that are listed in your report.
#11-Poor user engagement
User engagement is a growing factor in the ranking algorithm. Your site is always being compared to other websites (especially if it’s on the first page of results) to see how users are reacting to your content. If the user engagement on your website underperforms in comparison to the competition, your site will continue to slide down and off of the first page of search results.
Poor user engagement is indicated by the bounce rate, dwell time, pages visited per session and the expected click-through rate vs. actual click-through rate.
You can improve all user engagement stats by adding internal links, increasing page speed, adding images and features that would entice visitors deeper into your website.
Adding a video is a proven way to increase the length of time that visitors spend on your website.
Improving your headlines, meta-descriptions and adding structured data markup for rich results are also a way to improve the number of clicks that users are making to your site from the SERP. By making your search listing more attractive your page receives more attention, resulting in more clicks to your site.
Improving the overall user experience will increase the user engagement statistics your website generates and drive up your keyword ranking.
#12-There’s been a Google update
In the past, Google updates have turned the entire internet upside down. If Google implements a major update that changes how they rank websites, you could be looking at an algorithmic filter keeping you off of the first page of search results.
Updates like Panda represented major changes to how Google was assessing on-page content. Any website that was caught keyword stuffing was instantly penalized algorithmically and lost search visibility from its current rank.
Penguin changed how Google viewed high quality backlinks vs. low quality backlinks. Entire businesses were lost overnight when Penguin first hit the internet.
Avoid any drastic changes to your websites ranking by following Google’s best practice guidelines. If you’re not engaged in any blackhat tactics that violate these rules, you won’t be at risk to massive changes when an update kicks in.
#13-There’s a glitch in the matrix (Google of course!)
It’s been reported that Google updates the algorithm multiple times on a daily basis. Google is constantly adjusting the way its search engine is running. Just because they have a stranglehold on the search engine market doesn’t make them impervious to mistakes or glitches.
There are many moments throughout the year where rankings get completely shuffled for a period of time. In most instances the shift in rankings don’t last more than a day or two before returning to normal.
For more clarity on what’s happening in terms of changes in ranking, you can check out Mozcast. The tool tracks a large cross section of websites and bases its score on their fluctuation in rank. The measurement ranges from 1-100, where 100 is extremely volatile and 1 is absolutely no changes.
Nothing can prevent glitches from happening; you just need to ride them out. Eventually order is restored so before you go sounding alarms, check out the Mozcast to see if the entire internet is getting a shakedown.
#14-Poor choice of anchor text links
The anchor text you use when pointing links to your website can have a large impact on your search visibility and be a reason why your site doesn’t show up on Google. Too much of one type of anchor text can lead to over-optimization. Not enough descriptive anchor text and you come up short on properly optimizing your page.
Keep in mind that Google wants to see links build naturally. The Panda update is essentially a filter baked into the algorithm that corrects the excessive use of anchor text links with a drop in search visibility.
Although internal links may not have as much impact as external links, you should still be aware of the anchor text you use to link internal pages. Vary your anchor text links and avoid using too much of any one keyword.
For more guidance on how to structure your anchor text link ratios, it’s always a good idea to see how the top-ranking pages have done it. Learn how to use anchor text links to enhance the ranking power your pages have rather than hinder them.
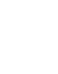
#15-You’re being too impatient
Just because you publish an article and stick a link on it doesn’t mean it will blaze its way to the top of the search results. Give your links and content a little time to be crawled, indexed and climb its way up in ranking.
A study was done on the number of pages that rank on the first page and the results showed that it’s difficult for pages to rank on the first page in less than a year.

Of course, there’s an exception to every rule. Low competition keywords can rank in as little as a few weeks if you have all the right pieces aligned.
The point is to have realistic expectations for where you’re currently ranking and where you should be ranking in the search results. If you’re not there yet, check yourself before you wreck yourself. You might not have given your work enough time to blossom, which is why your site doesn’t show up on Google.
Related reading: Benefits of Online Marketing For Businesses